Position Property in CSS
Static Positioning , Fixed Positioning , Relative Positioning ,Absolute Positioning , Sticky Positioning , Z-index
Position Property
The position CSS property determines how element positioned in a document.
The like top , right, bottom , and left determine the final location/offset/displaced location of positioned elements.
Static Positioning
It is set as the by default positioning in CSS. Element will follow normal document flow.

<body>
<div class="main"></div>
</body>
.main {
background-color: red;
height: 50px;
position: static;
}
Fixed Positioning
When we use ```position:fixed```` it will move our element out of the normal document flow. But element will be placed according/relative to the window of browser , no matter where parent element is. It will always visible on the viewport.(scroll with the page)
Before using position:fixed

After setting position:fixed to child element

After setting position:fixed to parent container as well as child element

<body>
<div class="main">
<div class="parent">
Container
<div class="first">first</div>
<div class="second">second</div>
..
</div>
</div>
</body>
.main {
border: 2px dotted black;
padding: 4rem;
position: static;
height: 100vh;
}
.parent {
padding: 1rem;
background-color: rgb(128, 131, 26);
position: fixed;
}
.first {
background-color: aqua;
position: fixed;
left: 8px;
top: 8px;
}
.second {
color: wheat;
background-color: blue;
}
Relative Positioning
It will not affect the normal document flow . It looks quite similar to normal document flow. We can move/displace our element with respect to its parent element.
After using relative positioning

.main {
border: 2px dotted black;
padding: 4rem;
position: static;
height: 100vh;
}
.parent {
padding: 1rem;
background-color: rgb(128, 131, 26);
}
.first {
background-color: aqua;
position: relative;
left: 34px;
top: 99px;
}
.second {
color: wheat;
background-color: blue;
}
Absolute Positioning
It will not always visible to viewport.(not scroll with the page)
It removes the element from its normal document flow. It displace the element with respect to the window of browser if its parent position is set to static.

But if we choose parent element parent element property set to any position other than static then it will placed the child relative /with respect to parent element

.main {
border: 2px dotted black;
padding: 4rem;
position: static;
height: 100vh;
}
.parent {
padding: 1rem;
background-color: rgb(128, 131, 26);
position: relative;
}
.first {
background-color: aqua;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
}
.second {
color: wheat;
background-color: blue;
}
Sticky Positioning
Element will act like they have static position when scrolling until they hit the top , left , right , bottom value.
After hitting that position it will scroll down but placing that element like position:fixed .

.main {
border: 2px dotted black;
padding: 4rem;
position: static;
height: 100vh;
}
.parent {
padding: 1rem;
background-color: rgb(128, 131, 26);
position: relative;
}
.first {
background-color: aqua;
position: sticky;
top: 10px;
left: 0;
}
.second {
color: wheat;
background-color: blue;
}
So far we have talked about left , right , top , bottom position alignment in 2D.
But if we want to add one more thing how close element is from us or how far is element is from us.
Z-index comes into picture
Z-index
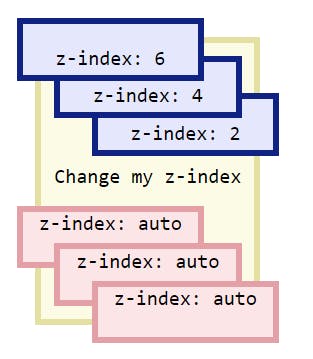 Above Image Source
Above Image Source
We can clearly see from the picture that more bigger the Z-index is , the more that element is close to us.
Before using Z-index

After using Z-index in first element

.main {
border: 2px dotted black;
padding: 4rem;
position: static;
height: 100vh;
}
.parent {
padding: 1rem;
background-color: rgb(128, 131, 26);
position: relative;
}
.first {
background-color: aqua;
z-index: 7;
position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 0;
}
.second {
position: relative;
color: wheat;
background-color: blue;
}
Comment if I have committed any mistake. Let's connect on my socials. I am always open for new opportunities , if I am free :P
